Industrial Camera Selection
Industrial cameras and industrial lenses are important components of machine vision systems, and the appropriate camera and lens determine the final effect of the system. Below we will introduce how to choose a suitable industrial camera, and the selection of industrial lenses will be discussed separately. If there are any errors, please feel free to communicate and correct them.
1. Choose the resolution of the camera based on the accuracy requirements of the test and the shooting field of view
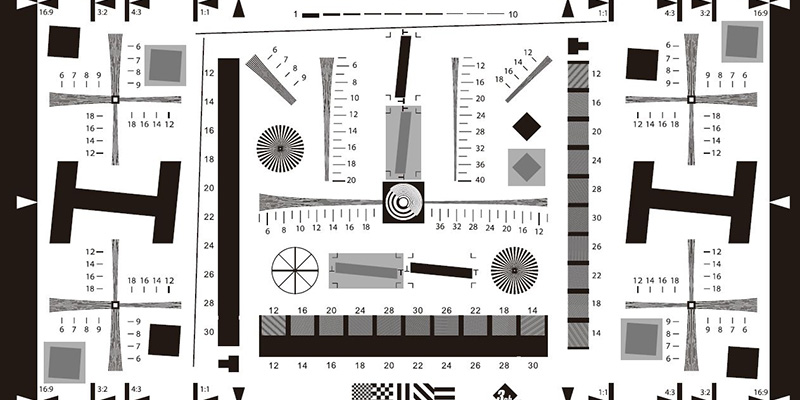
If you are doing dimensional measurements, this accuracy is your measurement accuracy. If you are doing defect identification, this accuracy is the minimum defect size you need to detect. The shooting field of view is the range within which the object being measured appears. For example, we need to measure the size of a workpiece placed on a conveyor belt, with a measurement accuracy requirement of 0.1mm. The size of the workpiece is 50mm * 50mm. The width of the conveyor belt is 68mm. Based on these conditions, we can determine that the testing accuracy is 0.1mm. The narrow edge of the shooting field of view should be 68mm. Instead of 50mm * 50mm. Because the workpiece is randomly placed on the conveyor belt. The sensor of a camera is usually 4:3, so the minimum field of view for shooting is 90mm * 68mm. So the minimum resolution of the camera should be at least: (90/0.1) * (68/0.1)=900 * 680, which is about 610000 pixels for a camera. That is to say, one pixel corresponds to one detection accuracy. So a camera with a minimum resolution of at least 610000 pixels is required. In practical applications, if one pixel corresponds to one accuracy, it is a considerable test of software algorithm ability, and the system is also extremely unstable. It is best to take 2 to 3 pixels corresponding to one accuracy unit. This requires at least 61 * 2, which is 1.22 million pixels, and it is rare to find cameras with 1.22 million pixels on the market. Therefore, we chose the commonly seen 1.3 million pixels in the market.
2、Choose the shutter mode of the camera based on whether the measured object is moving or not
Global shutter: The entire scene is exposed at the same time, suitable for capturing moving objects. Rolling shutter: The sensor scans and exposes each pixel line by line until all pixels are exposed, making it suitable for capturing stationary objects.
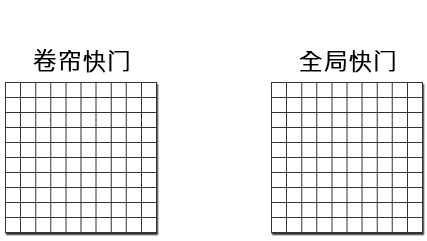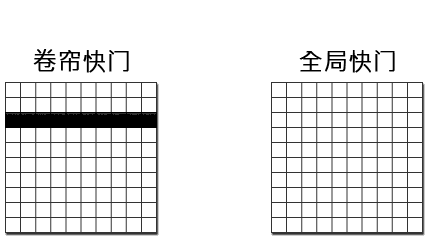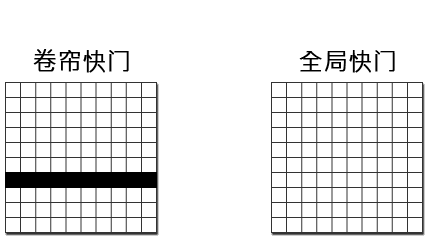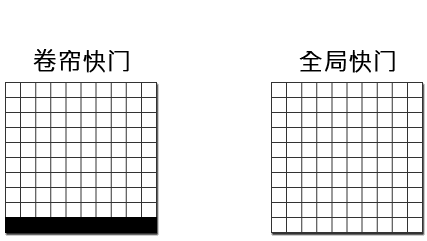

3、Determine the frame rate of the camera based on the motion speed of the subject being photographed
Motion speed/field of view=minimum frame rate Example: Continuing from the above example, if the motion speed of the conveyor belt is 1.7 meters per second. According to the formula, a frame rate of 25 FPS or above is sufficient.

4. Choose the image color of the camera
It is recommended to choose a color camera for all color related inspections, except for color recognition and color defect detection. Because for images of the same resolution, the detection accuracy of black and white images is better than that of color cameras. Black and white cameras have better contrast and sharpness than color cameras. Some black and white cameras can directly output grayscale images, which can be directly used for computational processing.
5. Select the sensor target of the camera
The size of the target surface will directly affect the size of the shooting field of view. In some situations where the working distance is limited, it is necessary to select the camera sensor target by combining the focal length and working distance. At the same focal length and working distance, the larger the sensor target, the greater the field of view.
6. Select camera interface based on frame rate, transmission distance, and economy
The commonly used camera interfaces in the current market are USB 2.0, USB 3.0, and GIGE Gigabit Ethernet interfaces. The theoretical bandwidth of USB2.0 is 450Mb/s, with a transmission distance of 5m. The theoretical bandwidth of USB3.0 is 5Gb/s, with a transmission distance of 5m. The theoretical bandwidth of the GIGE gigabit network interface is 1Gb/s, with a transmission distance of 100m. For example, following the example above, the customer chose a camera with a resolution of 1.3 million pixels and 25FPS or higher. Due to being a conveyor belt, the customer allows the computer to be placed nearby within 5 meters of the camera on the production line. So the bandwidth only needs about 260Mb/s. Taking these factors into consideration, we chose a USB 2.0 1.3 megapixel camera.
 Industrial cameras in measurin
Industrial cameras in measurin
 Industrial Camera Selection
Industrial Camera Selection
